Photograph (c) Margaret Smith
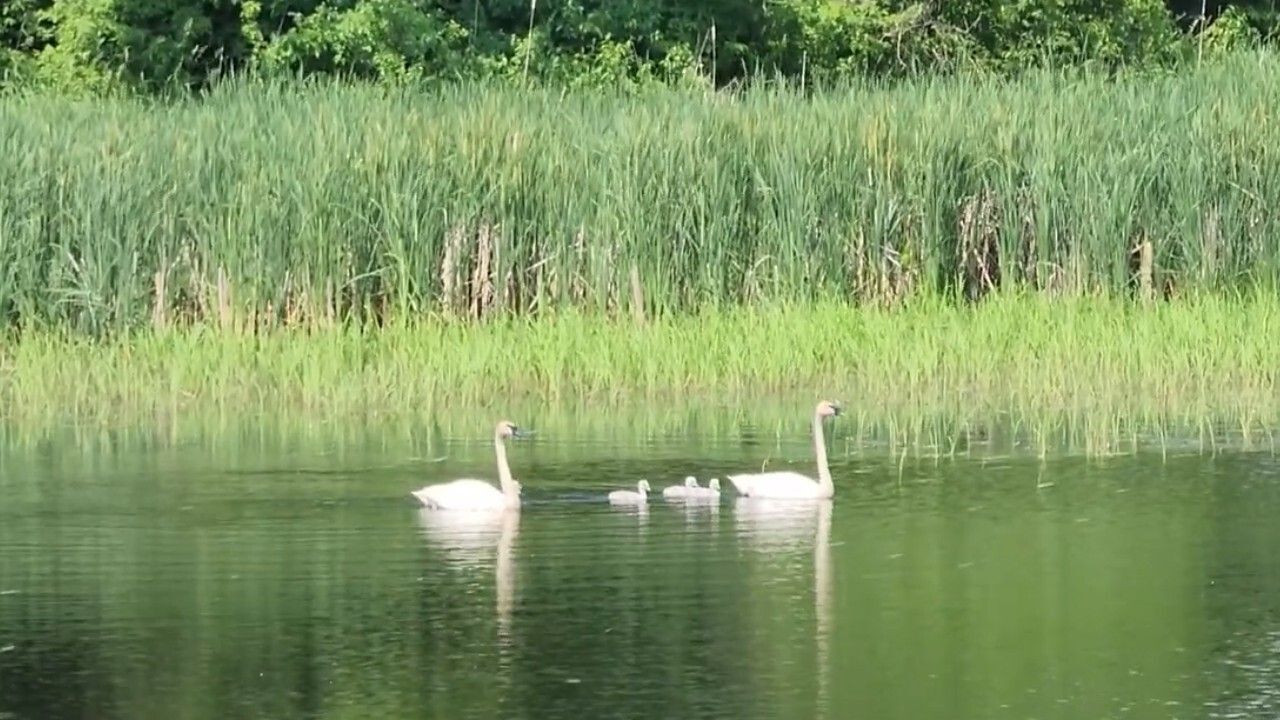
Wetlands are essential to all living things, and a vital habitat for trumpeter swans. Wetlands are also one of the most threatened ecosystems, at risk from pollution, climate change, and development.
Did you know?
- 40% of the world's species live or breed in wetlands.
- Wetlands are a source of clean drinking water.
- They can help reduce or prevent flooding.
- Some wetlands store greenhouse gases and can help mitigate climate change
- Wetlands support economies through sustainable fishing, agriculture, recreation and tourism.
Watch our webinar, An Introduction to Wetlands- the Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, to learn more about wetland benefits, the scale of wetland removal through policies in the US and Canada, and how you can help.
Wetlands, which include marshes, swamps, and bogs, are crucial ecosystems that provide a wide range of environmental benefits. Watch our webinar, An Introduction to Wetlands- the Good, the Bad, and the Ugly, to see the wide array of wetlands. Did you know even lakes are a kind of wetland?
Many species rely on wetlands for habitat, breeding grounds, and food sources. As wetlands vanish, these species are at risk of extinction, leading to a loss of biodiversity and disrupting fragile ecosystems.
People need wetlands. They are essential to having clean drinking water, and reducing damaging flooding.
- Wetlands are vital in maintaining water quality and regulating water flow.
- They act as natural filters, trapping pollutants and sediments before they reach larger bodies of water and underground aquifers.
- Wetlands also help prevent flooding by absorbing excess water during heavy rainfall and releasing it slowly over time.
- As wetlands disappear, the risk of water pollution and flooding increases.
How do you protect wetlands?
- Conservation measures such as creating protected areas
- Implementing sustainable land use practices
- Restoring degraded wetlands can help mitigate the loss of these critical habitats
- Collaboration among governments, environmental organizations, and local communities is key to safeguarding wetlands for future generations.
- Know how your representatives are voting on policies that impact wetlands.
The disappearance of wetlands requires our immediate attention and action. Protecting these vital ecosystems is not only essential for biodiversity and ecosystem health but also for the well-being of human communities that rely on the services provided by wetlands like clean drinking water and flood control.
You can help by (links are in Ways to Help, below):
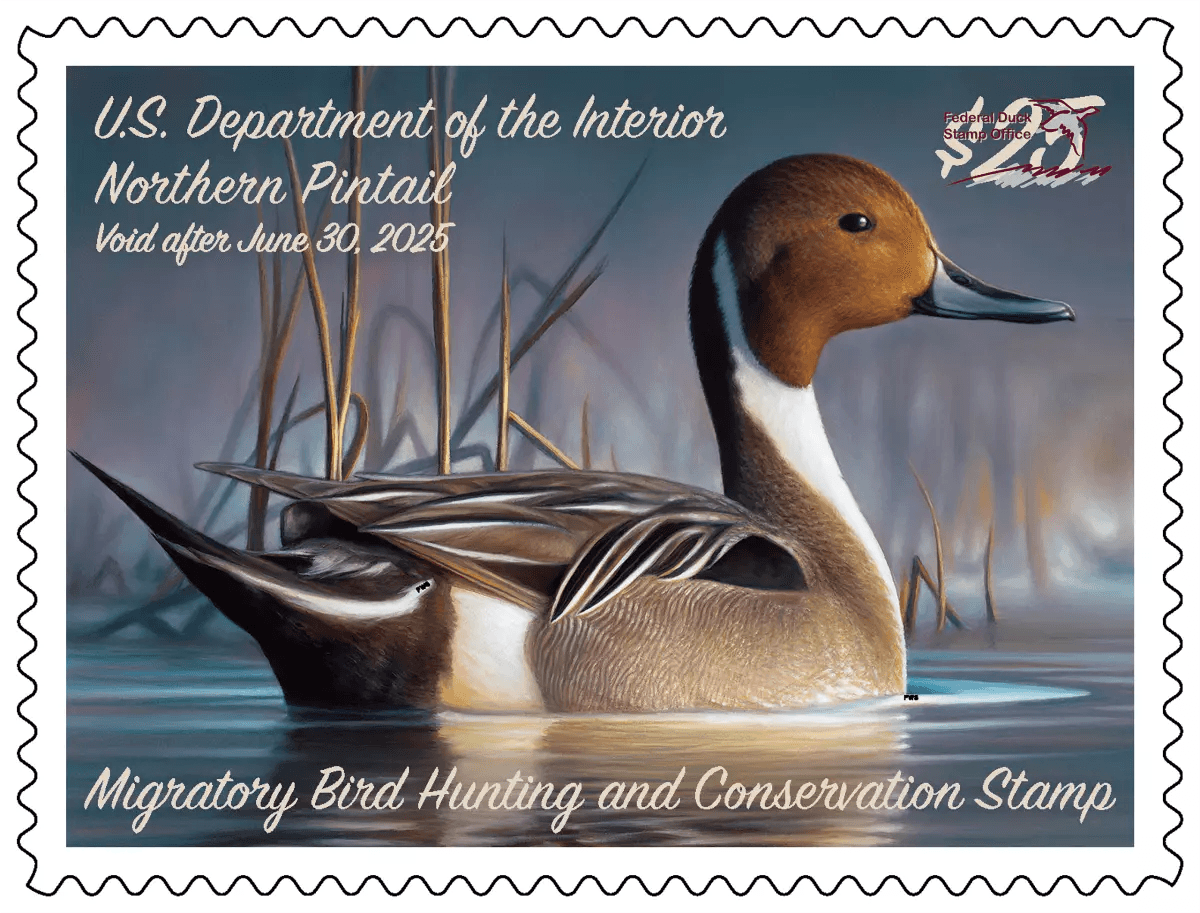
- Purchasing an annual US federal Duck Stamp, if you live in the US
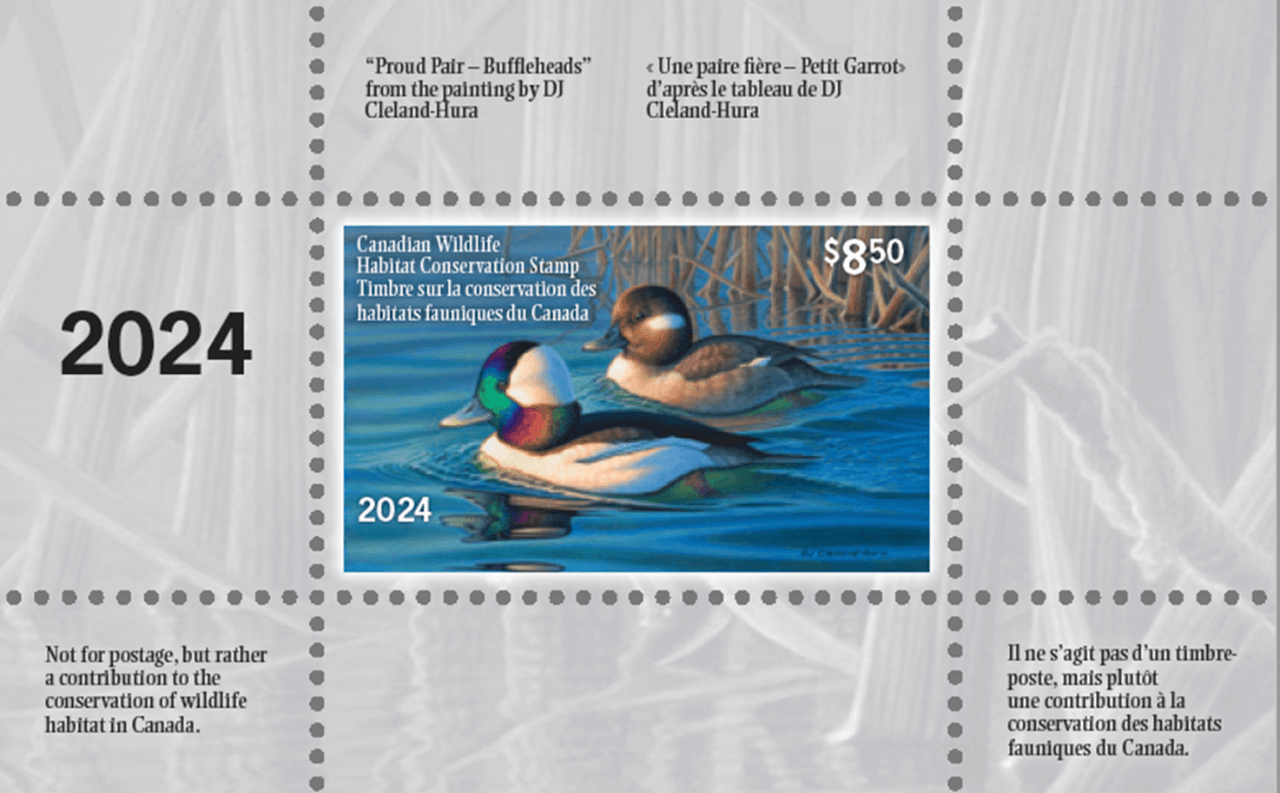
- Purchasing a Canadian Wildlife Habitat Conservation Stamp, if you live in Canada
- Be sure you know how your local legislators and representatives are voting nationally, state-wide or province- wide, and locally
- Make a donation to the North American Swan Fund of the Trumpeter Swan Society
- Wear and show your support by Trumpeting the Cause for Wetlands merchandise through our Conservation Gift Shop
- Share the importance of wetlands and their protection with children using our engaging and science- based activity books.